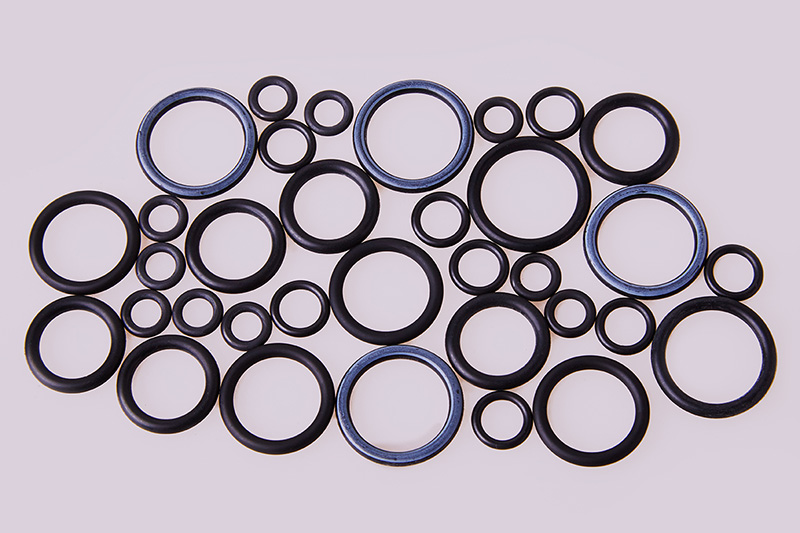
Endoscopy plays a crucial role in modern medicine, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize the interior of a patient’s body without invasive surgery. In this context, the O-ring is an essential component that enhances the functionality and reliability of endoscopic instruments. An O-ring is a simple yet effective sealing element, typically made of rubber or other elastomeric materials. Its primary purpose is to prevent leaks and maintain pressure in various mechanical systems, including those used in endoscopy.
In endoscopic procedures, maintaining a sterile environment is vital. Any leaks in the instruments can compromise the procedure’s success and the patient’s safety. Therefore, the role of O-rings becomes increasingly significant. By providing effective sealing, they help ensure that the instruments operate smoothly and efficiently, allowing for precise diagnosis and treatment.
The Importance of O-Rings in Endoscopic Instruments
O-rings serve several purposes in endoscopic instruments. First and foremost, they prevent fluid and gas leakage, ensuring that the equipment functions as intended. For example, during a procedure, the endoscope may need to insufflate gas to expand the area being examined. If the O-ring is compromised, gas may escape, leading to reduced visibility and potential complications.
Additionally, O-rings contribute to the durability and longevity of endoscopic instruments. By creating a reliable seal, they minimize wear and tear on the equipment, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Healthcare facilities can ensure their endoscopic tools remain in optimal condition, thereby enhancing patient care.
Types of O-Rings Used in Endoscopy
Various materials are used to manufacture O-rings, each with distinct properties suitable for different applications. In the context of endoscopy, the most commonly used materials include silicone, nitrile rubber, and fluorocarbon. Each material possesses unique advantages that cater to specific endoscopic requirements.
Silicone O-rings are known for their excellent temperature resistance and flexibility. They can withstand the high temperatures associated with sterilization processes, making them ideal for reusable endoscopy instruments. Nitrile rubber O-rings offer superior resistance to oils and chemicals, ensuring they maintain their integrity in various environments. Fluorocarbon O-rings, on the other hand, provide exceptional chemical resistance and are often used in high-performance applications.
The Manufacturing Process of O-Rings for Endoscopic Use
The manufacturing process of O-rings is critical to their effectiveness in sealing applications. Quality control is paramount, as even slight imperfections can lead to leaks and instrument failure. The process typically involves molding the O-rings from raw materials, followed by curing to enhance their mechanical properties.
Once produced, O-rings undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specific standards for sealing efficiency. Manufacturers conduct tests for dimensional accuracy, material hardness, and tensile strength. By adhering to these stringent guidelines, they ensure that the O-rings will perform reliably in endoscopic applications.
Common Challenges with O-Rings in Endoscopy
Despite their effectiveness, O-rings can face challenges that affect their performance in endoscopic instruments. For example, exposure to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals can degrade the material, leading to premature failure. Moreover, improper installation can also compromise the sealing capabilities of O-rings, resulting in leaks.
To mitigate these challenges, healthcare providers must regularly inspect and replace O-rings as part of their maintenance routines. By adhering to a proactive maintenance strategy, they can identify potential issues before they impact patient care. Furthermore, training personnel on the correct installation and handling of O-rings is essential to ensure optimal performance.
FAQs
What is the purpose of O-rings in endoscopy?
O-rings serve to create a seal in endoscopic instruments, preventing leaks and ensuring optimal performance during procedures.
How often should O-rings be replaced in endoscopic tools?
O-rings should be inspected regularly and replaced whenever signs of wear, such as cracking or deformation, are visible.
What materials are commonly used for O-rings in medical devices?
Silicone, nitrile rubber, and fluorocarbon are the most common materials used for O-rings in medical applications, including endoscopy.
Can O-rings be reused in endoscopic procedures?
While some O-rings are designed for reuse, they should be inspected thoroughly for wear and damage before being reused to ensure sealing efficiency.
How can I ensure the longevity of O-rings in endoscopic instruments?
To ensure O-rings last longer, follow proper maintenance protocols, regularly inspect them for wear, and replace them as needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the role of O-rings in endoscopic instruments cannot be overstated. They provide essential sealing capabilities that enhance the performance and safety of medical devices used in procedures. By preventing leaks and maintaining a sterile environment, O-rings contribute significantly to successful endoscopic outcomes.
Healthcare facilities must prioritize the quality and maintenance of O-rings to ensure their instruments remain reliable and effective. Continuous research and development in O-ring materials and manufacturing processes will further enhance their performance, supporting the ongoing advancement of endoscopic techniques.