How Precision CNC Turning Services Enable OEMs to Overcome Costly Manufacturing Errors and Boost Product Performance
Introduction
In today’s competitive scenario, the engineers of OEMs, as well as the purchasing managers, are confronted with a host of issues whenever they consider outsourcing the production of precision components. These could range from size variance, material scrap, and delays in delivery, essentially causing time and cost overrun, as well as impacting component reliability. These issues have their roots in suppliers’ lack of technical competence, absence of a proper quality control process, as well as ignorance of industry norms, like those of ISO.
This paper will discuss how precisely designed precision CNC turning services make use of cutting-edge technology, sophisticated quality controls, and analytical approaches for providing components right from the very start in a way that not only reduces the cost of ownership but further elevates product performance.
What Are the Basic Differences Between Normal Machining and Precise CNC Turning?
High accuracy CNC turning uses high-tech machinery and computer-controlled systems to ensure high accuracy. This is not true in conventional processes since they involve manual work. The two processes are therefore significant in their own fields despite their differing nature.
1. Equipment Accuracy and Technological Know-how
Conventional machining employs traditional lathe machines with very limited automation, whereas precise CNC turning services involve multi-axis CNC lathe machines with high-resolution encoders and dynamic tool turrets. The turning process requires precise control and alignment of the tool onto the workpiece to produce dimensions with an accuracy of ±0.005mm. In this regard, for example, the ASME Y14.5 standard incorporates strict rules of geometric dimensioning and tolerancing. Precision turning strictly follows these rules.
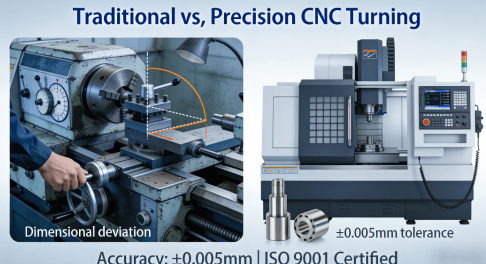
2. Process Control and Standardization
Whereas conventional machining might not be addressed by structured monitoring, precision turning utilizes Statistical Process Control directly, whereby the essential variables such as the wear of the tools and the temperature are continuously observed. As has been explained in various resources, including a guide on precision CNC turning services, control of the process is the key factor that can control variability and ensure sound quality.
3. Consistency and Tolerance Adherence
The standard processes may also experience inconsistent startup conditions. However, in the case of precision CNC turning, it ensures the same datum all through the manufacturing process. This ensures the avoidance of accumulated errors in complicated rotational components. The use of automated feedback loops in high-precision turning services enables the production of highly accurate components.
How Does the CNC Turning Process Integrate Planning, Execution, and Verification for Zero-Defect Results?
Optimization, monitoring, and inspection are perfectly integrated in this process to ensure quality right from the onset. This helps to eliminate flaws or mistakes.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Planning: This begins with a detailed design reviewto optimize part geometry for manufacturability. Engineers consider factors like wall thickness and feature accessibility to avoid machined part problems. DFM suggestions, like harmonizing radii values, can help bypass expensive redesigning down the line and are consistent with ISO 9001 for risk-based thinking to address Failure Issues.
- CAM Programming and Execution: The latest CAM softwareenables efficient tool paths from models in a CAD system, optimizing factors such as feed rate and depth of cut. While executing this process, real-time monitoring is done to check tool status and spindle use, which further facilitates adaptability. For instance, sensors in this process allow for tool changeovers even before an error happens, and zero-defect manufacturing is ensured.
- Verification and Quality Assurance: After machining, the components are inspected for accuracy through the use of CMMs and optical comparators. Results of the tests are stored as part of traceability, helping manufacturers comply with requirements like ISO 9001 certification.In scalable manufacturing, advanced suppliers have incorporated validation processes into their CNC turning process descriptions.
What Key Advantages Do Precision Turning Services Offer in OEM Projects for Cost and Efficiency?
It enables waste minimization, whilst reducing total cost of ownership, and improves product capability and life. The OEMs benefit from faster time-to-market and improved reliability.
1. Minimizing Total Cost of Ownership
There is a reduction in material waste of over 15% due to precision turning, as this results in a reduction in the number of scraps and repairs. Single-source traceability also makes supply chain management simpler, resulting in a cost reduction related to paperwork. Allowing a medical device manufacturer to change suppliers to a certified one saved the company 20% on its own due to the cost-effective nature of CNC turning services.
2. Improved Supply Chain Reliability
The precision providers ensure transparency in schedules and timely notifications, hence overcoming delays. The overall effect of the integrated quality control is that components are supplied and ready for assembly, hence accelerating time to market. This is essential in JIT-manufactured production environments where, if an equipment fails, an entire production line could be paralyzed.
3. Improved Functionality and Longevity
It has been seen that accuracy machined components provide improved fatigue and compatibility resistance properties. There would be improved lifespan and reduced claims under the warranty period for components if accuracy machining is implemented in the automobile industry. This is because micron variation has a crucial role to play in the failure of components.
How Do Material Selection and Tolerance Specifications Influence Prices of CNC Turning Services and Outcomes of Projects?
Material choice and tolerance levels have direct implications on expenditure. But by proper utilization of DFM, there can be a reduction in these costs without having any impact on functionality or performance. This may help original equipment manufacturers take proper decisions.
- Characteristics of Materials and Machinability: The machinability of aluminum and stainless steel is good. However, for exotic materialslike titanium, special cutting tools and slower speeds are required due to high production costs. In CNC turning processes, it becomes appropriate to ensure that performance and economical considerations are aligned when making selections of materials. Scientific literature citations from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) are helpful in understanding materials and their properties.
- Tolerance Tightness and Cost Effects: Tighter tolerances(e.g., ±0.002 mm) imply the use of more advanced equipment and higher processing time and therefore more expensive components. Nevertheless, tolerance usage with a focus on critical parameters will provide the best costing for CNC turning with respect to functionality and due to DFM analysis; relaxation of tolerances will be detected.
- Considerations of Volume and Surface Finish: Economies of scaleare achieved for bulk production, but for smaller productions, modular tooling is used. Surface finishing operations like anodizing could be an additional expense, but they provide enhanced properties of resistance to corrosion. Understanding the aforementioned factors very well helps in the right positioning of specifications.
What is the Function of Quality Assurance in High-Risk Industries Such As Aerospace and Medical Regarding Compliance?
The QA system supports different processes such as inspection and documentation certifications. The processes ensure fewer risks are involved. The processes comply with global standards. There is also emphasis on continuous improvement.
1. In-Process Inspection and Documentation
QA systems make use of probes and vision systems during the production process to verify basic parameters. The results of these tests are then recorded in the certificates of conformity (CoC) documents. It is very important that these processes take place within the regulated industries; auditors require proof of conformity.
2. Certification Frameworks & Risk Mitigation
Other benchmarks like AS9100D, which is used in the aerospace industry, and ISO 13485, used in the medical device industry, embody high process controls. Organisations with such certifications indicate compliance with global requirements, hence are not a high risk for the OEM. For example, IATF 16949 certification for precision engineering capabilities in the motor industry.
3. Lifecycle Management & Continuous Improvement
Besides the need for initial compliance, the premium companies have also taken other measures such as audit and corrective action plans. For example, a firm that produces aerospace components avoided potential recall situations by using trend analysis before the creation of the tool.
In What Ways Can Car Manufacturers Implement DFM Optimization to Reduce Turning Cost Without Affecting Quality?
The objective of DFM optimization is design standardization, use of tolerances, and coordination with suppliers to minimize cost to a desired quality of products. This encourages innovation.
1. Design Standardization & Feature Optimization
Hole sizes and corner radii can be standardized, ensuring easier tooling or changeovers. Hence, DFM optimization will result in options for a symmetrical design that enhances machining stability. Institutions such as Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME) offer recommendations for best practices, incorporating trade-offs between complexity and the costs involved.
2. Strategic Tolerance Application
Not all features need to have tight tolerances. Selecting dimensions for classification on the basis of functionality makes it possible to define critical areas with precision. In turn, combining advanced CAM programming with this approach helps decrease machining time by up to 30% without compromising on performance.
3. Collaborative Supplier Engagement
Early integration with Turning Experts during design phase enables manufacturability feedback in real-time. Design workshops for manufacturability improve opportunities for combining components and optimizing designs with reduced geometries, thus minimizing materials and costs. For example, a consumer product company minimized components by 25% for improved DFM designs.
Conclusion
Precision CNC Turning Solutions enable OEMs to mitigate product manufacturing errors through deliberate processes, quality checks, and partnership approaches. Important points to learn are how planners and verifiers must work together, how optimizing DFM pays off economically, and how accredited suppliers mitigate risks. By embracing such philosophies, product reliability, speed to market, and total cost of ownership increase for OEMs.
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical tolerance possible with a high-precision CNC turning operation?
A: Precision CNC turning can achieve a tolerance of ±0.005mm, thanks to multi-axis machining equipment. Standards, such as ASME Y14.5, provide geometric requirements for manufacturing components with a specific set of requirements, especially for industries such as the aerospace industry or the production of medical equipment.
Q2: What are the differences in precision turning and milling for intricate parts?
A: Milling is better suited for multi-faced components, whereas turning is more suited for rotor-based elements like shafts and possesses greater advantages concerning concentricity and cycle times because precision turning involves continuous verification, whereas milling involves several setups, which can lead to errors.
Q3: What materials should be considered for high-volume CNC turning operations?
A: Aluminum alloys and stainless steel are common due to their ease of machining and strength. Titanium alloys are preferable for high-stress usage. Material cost and time are optimized using DFM based on NIST information.
Q4: What is the advantage of small batch production in precision turning when the cost is not considerable?
A: Smaller batches utilize automated systems and modular tooling, making production cheaper on a per-unit basis. The companies rely on data analytics to keep costs low and can sometimes accomplish economies of scale.
Q5: What certifications should a good supplier of turned parts have?
A: The major certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management system, IATF16949 for the automotive industry, and AS9100D for aerospace industry. These help to comply with international norms and reduce concerns related to compliance.
Author Bio
The author is an expert in precision manufacturing at LS Manufacturing, a firm that assists engineers or researchers in overcoming tough part design issues in the areas of Aerospace, Medical, and Automotive. The firm is certified in IATF 16949 and AS9100D. To know more, contact them today and get a free, no-obligation project consultation. Make your idea into an economical fact.






