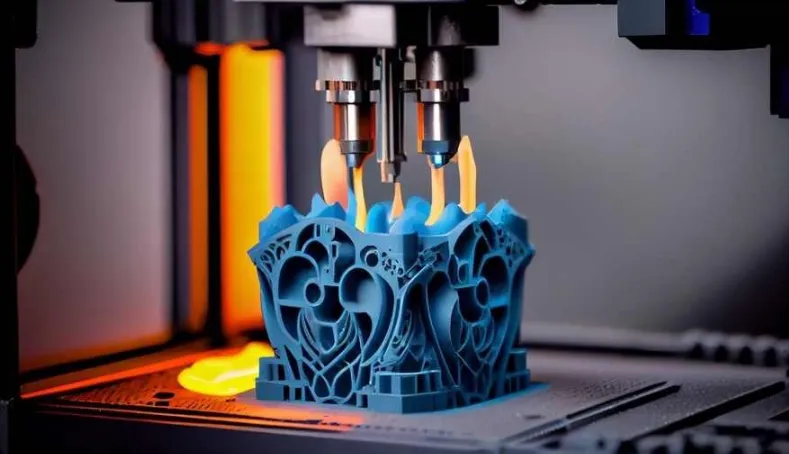
By radically altering the logic of conventional manufacturing, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has allowed products to be made that are unprecedentedly intricate, flexible, and useful. Unlike subtractive manufacturing, where parts are removed to create the shape one wants, this new technology creates objects from digital designs, one layer at a time.
This activity disrupts markets, spurs creativity, and resolves industrial challenges in healthcare, aerospace, automobile, fashion, and construction. For example, new technologies have led to interesting applications, such as those seen in the casino iGaming industries offering promos like the Vulkan Bet No Deposit Bonus to attract players to check out new gaming tech additions. This article outlines the latest methods, uses, advantages, and opportunities of printing in production.
What Is 3D Printing? Understand the Fundamentals
At its heart, this concept is a manufacturing technique that converts computer models into tangible objects. It creates highly complex and accurate designs that conventional methods can’t make, like stacking materials over each other. More excellent applications across industries have been found because of the vast array of possible materials that can be used in this type of printing, ranging from metals and polymers to ceramics and lifeforms.
Since this procedure only consumes the material needed for a product, it is a more effective and environmentally friendly option than traditional manufacturing, which often creates excess waste. It allows designers and engineers to test complicated ideas with great accuracy.
Key Advancements in 3D Printing Manufacturing
This kind of printing has produced disruptive products that challenged traditional manufacturing methods. Beyond facilitating production, these changes have created new opportunities for sustainability, customization, and design. Here, we explore the key developments shaping the future of this concept in manufacturing.
- Rapid Prototyping;
- Customization at Scale;
- Low-Volume Production;
- Complex Geometries;
- Sustainable Manufacturing.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is one of the most critical gains this procedure provides. Prototyping methods used in the past can create A successful model in weeks or months. But this concept speeds this up tremendously. Product development times are significantly reduced because designers can rapidly iterate, test, and optimize their ideas within a few days. In the case of automobiles, for example, the concept allows rapid manufacturing of prototype components, allowing engineers to validate their performance, fit, and function before mass production.
Customization at Scale
Customization is another fantastic thing about this innovation. Traditional methods require expensive moulds and machinery to make bespoke products, so this procedure creates custom designs without extra set-up. It is used in medicine to design each patient’s custom surgical equipment, implants, and prostheses. Along with enhancing patient outcomes, this personalized approach boosts productivity and reduces costs.
Low-Volume Production
It is an affordable solution for industries requiring short production runs. Traditional manufacturing methods are often prohibitively expensive in a low-volume environment, and this procedure thrives in these circumstances. This power is a boon to small-scale businesses (luxury products, for instance, or custom machinery parts), where companies can produce limited numbers without paying a high price.
Complex Geometries
Rich patterns or underlying structures are often unreachable through conventional methods of production. This concept emerges here, as manufacturers can manufacture parts that feature complex lattice structures and shapes. This ability is instrumental in the airplane industry, where strong, lightweight parts are vital for higher fuel efficiency and lower emissions. It permits engineers to break free from the limitations of design.
Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability is one of the defining advantages. More so than standard processes, it dramatically reduces waste by consuming the required material per unit. Secondly, recycled materials can be recycled as feedstock for printing due to recycling technologies. Because biodegradable and renewable materials are also being explored, it becomes crucial to sustainable production.
Application of This Concept Across Industries
For this flexibility, this manner of printing has revolutionized various industries, redefining how goods are designed, produced, and delivered. It has indivisible and paradigm-changing applications, from construction to medicine. Here are some examples of how this concept drives innovation and transforms core industries.
Medical Care
It opened up a new generation of patient-centred solutions in medicine. The technology changes how surgeries are performed and enhances clinical outcomes, from bio-printed tissues and organ simulators to orthopedic implants and bespoke prostheses. Surgeons can improve accuracy and reduce risk by replicating complicated procedures on 3D-printed models.
Automotive and Aerospace
The aerospace and automotive industries have embraced it because this procedure allows you to produce thin, robust, and efficient components. Automotive companies use the method to make prototypes and custom assemblies, and aerospace manufacturers use fuel-efficient components. These advances translate into more innovation, higher performance, and reduced costs.
Building
This concept transforms the construction industry since it allows whole buildings to be constructed. It saves labour and material costs while accelerating the project cycle. This style of printing is already being used to produce low-cost housing units in low-income countries as a solution to the housing shortage on a long-term basis.
Consumer Goods and Fashion
The procedure helps create products of a specific kind that are customizable for consumers and fashion designers. Tech allows companies to meet personal tastes and desires — from 3D-printed shoes and jewelry to handmade sunglasses and furniture. This level of personalization increases brand awareness and increases customer satisfaction.
Empowering Industries Through 3D Printing Technologies
This printing type disrupts manufacturing with innovations that solve traditional issues and open up new possibilities. From high-end architecture and environmentally sound manufacturing to quick prototyping and personalization, technology is changing industries across the globe. Despite so many challenges, the ongoing advancement of this concept promises a time when innovation, efficiency, and sustainability will coalesce to redefine how goods are produced, consumed, and sold. 3D printing presents an opportunity and a necessity for innovation for industries and businesses keen to remain ahead of the game.