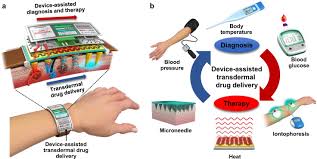
Innovations in drug delivery have propelled the development of novel technologies aimed at enhancing therapeutic efficacy, patient convenience, and treatment outcomes. Among these breakthroughs, dermal delivery have emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the administration of medications through the skin.
Understanding Dermal Delivery Devices
Dermal delivery devices represent a specialized class of apparatus designed to facilitate the transdermal administration of medications. Unlike traditional oral medications or injections, which rely on systemic circulation, dermal delivery devices offer a localized approach, delivering drugs directly to the target tissue or organ with precision and efficiency. These devices may utilize micro-needles, transdermal patches, or advanced controlled delivery mechanisms to achieve optimal drug delivery.
Applications Across Healthcare
The versatility of dermal delivery devices extends across various medical specialties, unlocking a multitude of applications:
Transdermal Drug Delivery: Dermal delivery devices are widely employed for transdermal drug delivery, enabling the administration of medications for pain management, hormone replacement therapy, nicotine cessation, and motion sickness prevention, among other indications.
Vaccination: Micro-needle-based dermal delivery devices hold promise for vaccine administration, offering a painless and needle-free alternative to traditional injections. By delivering vaccines directly to immune-rich skin layers, these devices enhance immune responses and vaccine efficacy.
Dermatological Treatments: In dermatology, dermal delivery devices are utilized for the localized treatment of skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, acne, and alopecia. By targeting the affected skin directly, these devices minimize systemic exposure to medications and reduce the risk of adverse effects.
Key Components and Mechanisms
Dermal delivery devices comprise several key components that contribute to their functionality and effectiveness:
Micro-needles or Transdermal Patches: Many dermal delivery devices utilize micro-needles or transdermal patches to facilitate drug delivery through the skin. Micro-needles create micro-channels in the skin, while transdermal patches contain drug-loaded matrices or reservoirs for controlled drug release.
Drug Reservoir or Cartridge: The device may incorporate a drug reservoir or cartridge containing the medication to be administered. This ensures a consistent and controlled release of the drug, optimizing therapeutic efficacy.
Controlled Delivery Mechanism: Advanced dermal delivery devices feature precise mechanisms for controlling the rate and duration of drug delivery. This may include programmable pumps, osmotic systems, or temperature-sensitive formulations that modulate drug release based on specific cues.
Advantages and Future Outlook
The adoption of dermal delivery devices offers numerous advantages to patients, healthcare providers, and pharmaceutical manufacturers:
Improved Patient Compliance: Dermal delivery devices offer non-invasive, painless, and convenient administration routes, improving patient acceptance and compliance with medication regimens.
Enhanced Therapeutic Outcomes: By delivering medications directly to the target site, dermal delivery devices optimize drug concentrations and minimize systemic exposure, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes and reduced side effects.
Advancements in Formulation Design: The development of dermal delivery devices has spurred innovations in formulation design, paving the way for novel drug formulations with enhanced stability, bioavailability, and patient convenience.
As research and development in dermal delivery devices continue to advance, the future holds immense promise for personalized and precision medicine approaches. With ongoing innovations in micro-needle technology, transdermal patch design, and controlled delivery mechanisms, dermal delivery devices are poised to play an increasingly prominent role in shaping the future of healthcare delivery and pharmaceutical innovation.
More Read About: baddiehub