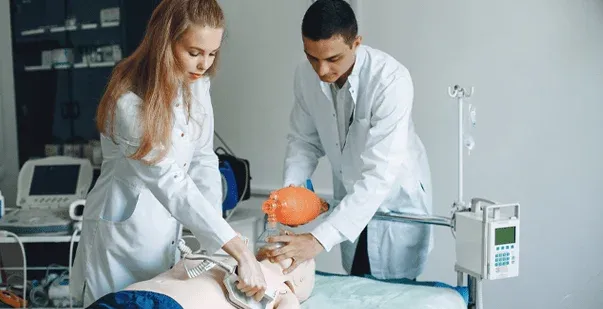
Cardiac arrest is a serious medical emergency where the heart suddenly stops beating. This means the heart is no longer pumping blood to the rest of the body, leading to a quick loss of consciousness and, if untreated, death. In these critical moments, immediate action is crucial. While CPR (chest compressions and rescue breaths) is vital, oxygen therapy plays a big role in improving the chances of survival by providing oxygen to the brain and other organs.
Proper training in oxygen therapy, like the Certified advanced resuscitation and oxygen therapy training in Brisbane, helps healthcare professionals and first responders save lives.
What is Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops working due to an issue with its electrical system, causing an irregular heartbeat or complete heart stoppage. This is different from a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked. In cardiac arrest, the heart cannot pump blood to the brain, lungs, and other organs. Without immediate treatment, the person can die within minutes. Signs of cardiac arrest include sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing, and loss of consciousness.
In situations like this, CPR and defibrillation (electric shocks to the heart) are critical to keep the person alive until medical help arrives. But along with CPR, oxygen therapy is key to helping the body stay alive, as it ensures the organs keep getting oxygen during the emergency.
How Does Oxygen Therapy Work?
Oxygen therapy is a way to give patients extra oxygen when their bodies can’t get enough from breathing alone. In cardiac arrest, the heart’s ability to circulate oxygen-rich blood is severely affected, causing oxygen levels in the brain and other organs to drop dangerously low. If the brain is deprived of oxygen for too long, lasting damage can occur, making survival or full recovery more difficult.
Oxygen therapy helps by increasing the amount of oxygen in the bloodstream, which keeps vital organs like the brain alive. In emergencies like cardiac arrest, oxygen is typically given using masks or breathing tubes.
Learning how to use oxygen therapy correctly is an important skill that requires proper training. Programs such as advanced first aid training classes provide individuals with the knowledge and skills to use oxygen effectively in emergency situations, helping improve patient outcomes.
Oxygen and CPR: Working Together
CPR, which combines chest compressions and rescue breaths, helps keep blood flowing and provides oxygen to the body during cardiac arrest. While chest compressions are critical for maintaining circulation, rescue breaths make sure that oxygen enters the lungs and reaches the blood.
When oxygen therapy is used alongside CPR, it can greatly improve the person’s chances of survival. Normally, the air we breathe contains around 21% oxygen, but oxygen therapy can deliver up to 100% oxygen, ensuring that the brain and organs get the oxygen they need.
During CPR, oxygen therapy can be delivered through:
- Bag-Valve Mask (BVM): A device that is squeezed by hand to push air and oxygen into the patient’s lungs.
- Airway Devices: Tools such as oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways help keep the airway open, allowing oxygen to be delivered effectively.
By combining CPR with oxygen therapy, rescuers can significantly increase the chances of the patient surviving cardiac arrest.
Advanced Life Support (ALS) and Oxygen Therapy
Once basic CPR is done, Advanced Life Support (ALS) takes over. ALS is usually provided by trained healthcare professionals and includes more complex treatments like defibrillation, airway management, and medication. Oxygen therapy is still a key part of ALS, as it helps keep the brain and heart alive until the heart’s function is restored.
In ALS, oxygen can be delivered through:
- Endotracheal Intubation: A tube is inserted into the windpipe (trachea) to keep the airway open and provide a direct route for oxygen.
- Positive Pressure Ventilation: Oxygen is delivered through machines or manual devices to ensure the patient gets enough air even if they can’t breathe on their own.
In ALS, the goal is to prevent brain damage by making sure the brain and heart get enough oxygen, especially after blood flow has been restored.
Oxygen Therapy After Cardiac Arrest
Even after the heart has been restarted, patients need continued care to avoid damage caused by oxygen deprivation. This is where post-resuscitation oxygen therapy comes in. Once the heart is beating again, the brain and other organs may still need extra oxygen to fully recover.
Post-resuscitation oxygen therapy may include:
- Oxygen Masks or Nasal Cannula: These devices are used to provide a steady flow of oxygen to the patient after resuscitation.
- Monitoring Oxygen Levels: Doctors and nurses use devices like pulse oximeters to measure how much oxygen is in the patient’s blood, ensuring they get the right amount.
In some cases, restoring blood flow too quickly can cause additional problems like swelling or tissue damage. Careful oxygen therapy can help prevent these issues and aid in the patient’s recovery.
Oxygen Therapy Outside of Hospitals
Most cardiac arrests occur outside hospitals, so first responders like paramedics, firefighters, or even trained bystanders need to know how to use oxygen therapy. Portable oxygen systems allow responders to give oxygen to patients before they reach the hospital.
Programs like Certified advanced resuscitation and oxygen therapy training in Brisbane teach people how to use portable oxygen systems in emergency situations. These courses cover how to operate oxygen tanks, masks, and resuscitation bags so responders can act quickly and effectively.
Why Training in Oxygen Therapy is Important
Since oxygen therapy is so important during cardiac arrest, proper training is essential for those involved in emergency care. Advanced first aid and resuscitation training courses teach healthcare professionals and first responders the skills they need to provide life-saving oxygen during an emergency. Training includes:
- Understanding oxygen’s role: How oxygen helps the brain and organs during cardiac arrest.
- Airway management: How to keep the patient’s airway open so that oxygen can be delivered.
- Using oxygen equipment: Hands-on practice with oxygen delivery devices like masks and bags.
Attending advanced first aid training classes is a good way for people to learn how to handle emergencies and perform life-saving procedures effectively.
Conclusion
Oxygen therapy is an essential part of managing cardiac arrests. It helps to maintain the oxygen supply to the brain and organs, improving the chances of survival and recovery. Whether during CPR or in advanced life support, oxygen therapy helps prevent damage from oxygen deprivation.
Proper training in oxygen therapy is vital, as it ensures that healthcare professionals and first responders can deliver oxygen effectively in life-threatening situations.
In emergency situations like cardiac arrest, combining CPR, defibrillation, and oxygen therapy is crucial. By ensuring that oxygen continues to reach vital organs, first responders can make a significant difference in the patient’s chances of survival.